Source: ASX data
Source: ASX data
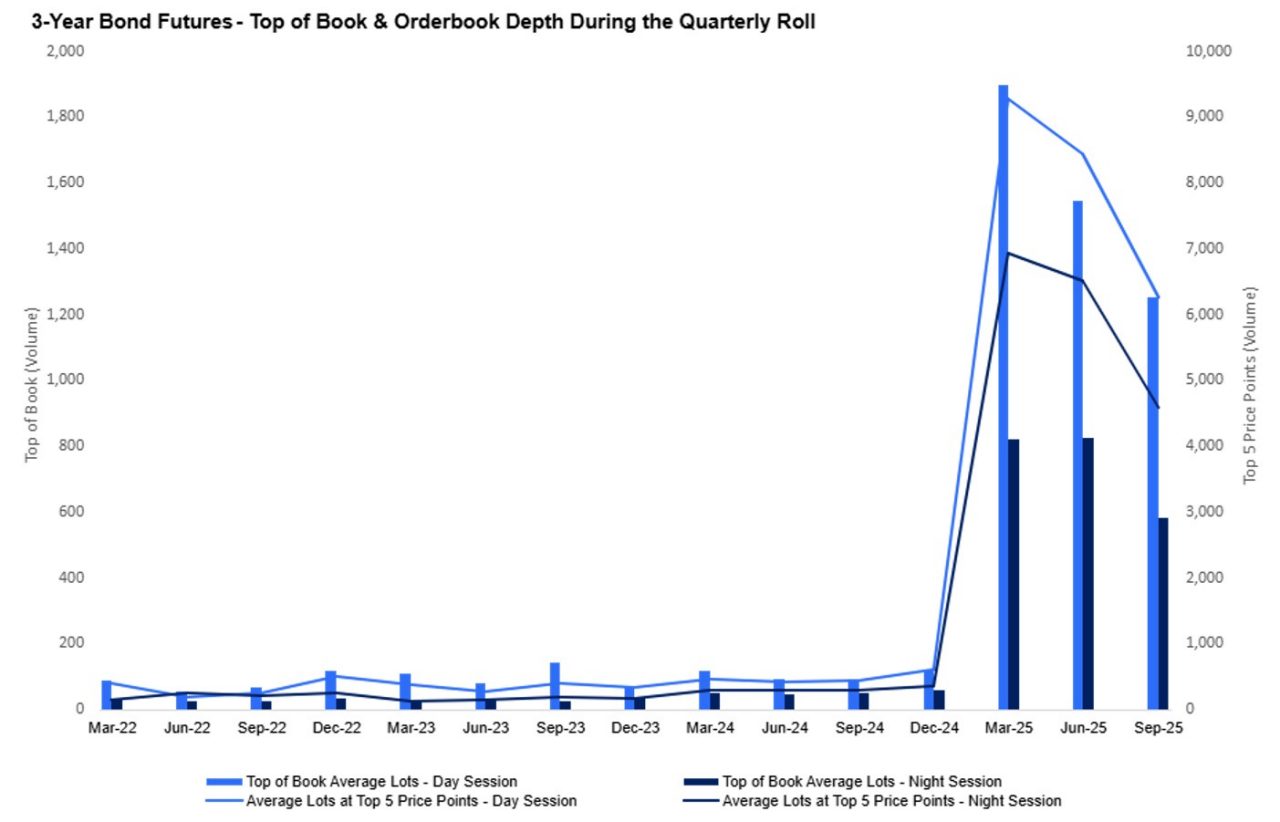
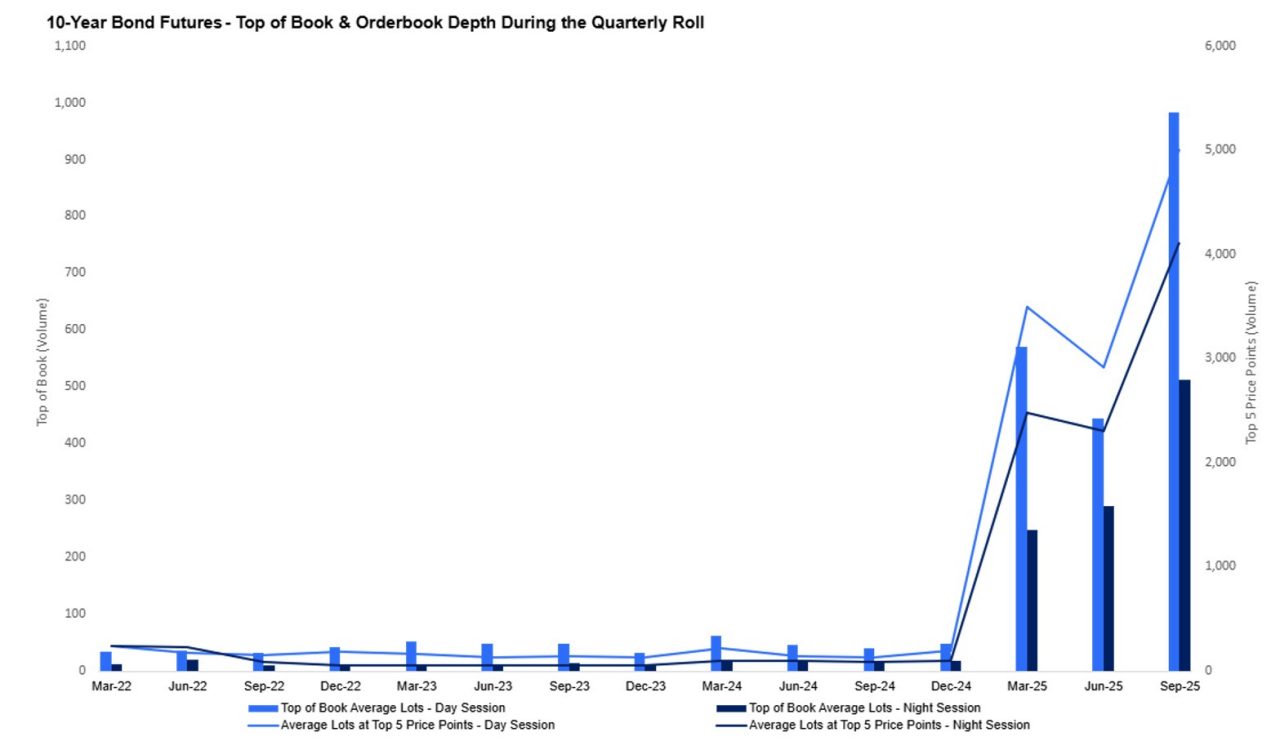
The benefits of the delinking initiative were immediate and sustained, with significant liquidity improvements observed across both day and night trading sessions. These gains have persisted through the June and September 2025 roll periods, marking a clear improvement to the liquidity conditions seen prior to implementation.
Independent analysis published by the Reserve Bank of Australia provides further validation of the liquidity improvements achieved through the Bond Futures Delinking initiative. The research discussion paper, "Back to the Futures: Liquidity in Australian Bond Futures amid Market-Moving Events since COVID-19" [2] authored by Finlay, Jackman and Titkov 2025, found that price impact (measuring the price move in basis points per billion dollars of net flow), declined following the March 2025 delinking. Specifically, deterioration in price impact during the roll period in the 3-Year Bond Futures fell to 1.1 bps, while in the 10-Year Bond Futures it dropped to 1.9 bps as compared to 3-6 bps in previous periods (Finlay, Jackman and Titkov, 2025 pp42/50).
Arguably, the combined improvements to top of book liquidity and order-book depth has contributed to a reduction in price impact during the roll for outright contracts. Enhanced liquidity allows the market to absorb larger trades with less price movement, resulting in lower slippage and more efficient execution to benefit overall market quality during the quarterly roll periods.
Growth in outright market trading activity
In fostering deeper liquidity in the outright market, the delinking initiative has notably improved the ability for participants to complete hedging and risk management transactions efficiently during the roll period, driving broader market participation and an increase in overall market turnover during the roll period.
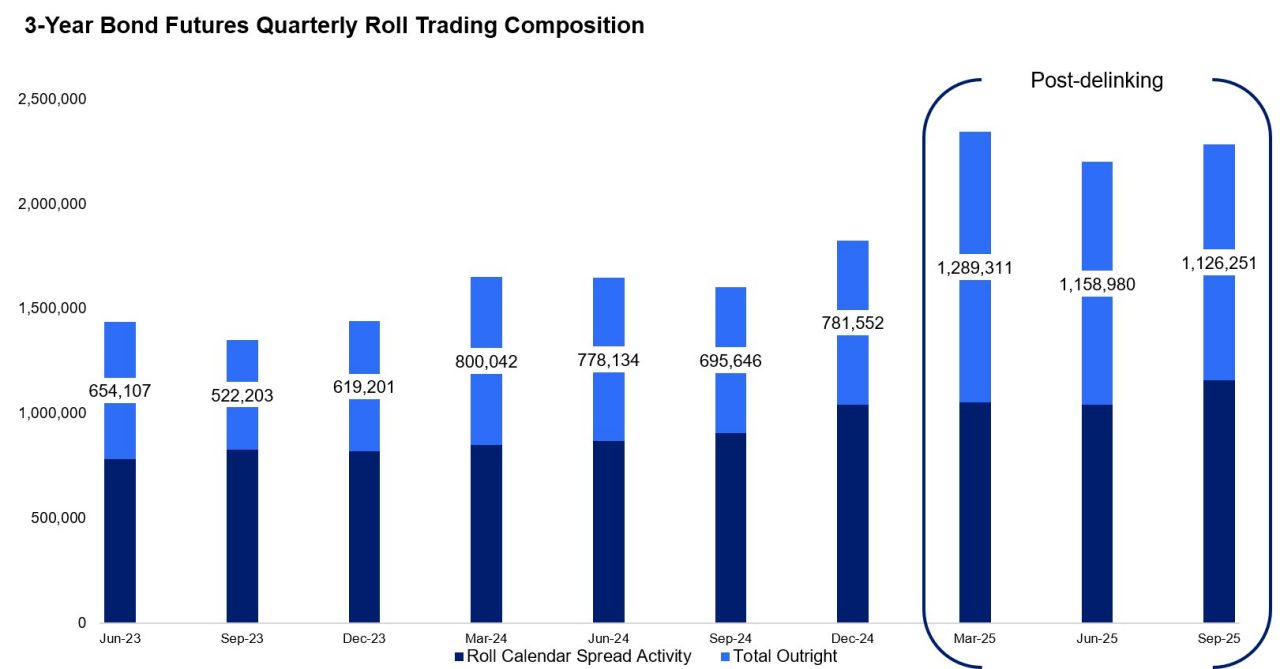
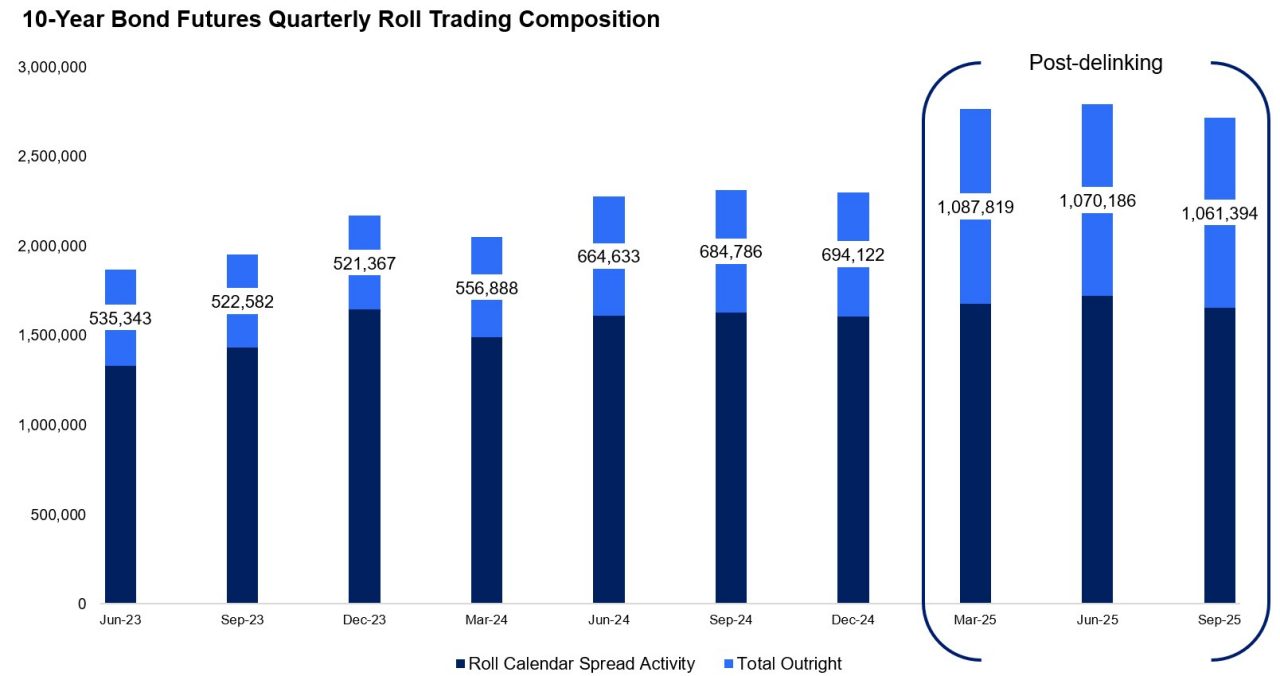
In the 3-Year Bond Futures, total outright volumes during recent roll periods have consistently exceeded the long-term average of 587,000 lots (measured since September 2020). Immediately following the delinking initiative, outright activity more than doubled against this historical measure, where total outright volumes during the March, June and September 2025 roll periods averaged 1,190,000 lots. Similarly, in the 10-Year Bond Futures, outright activity during the roll period has continually exceeded 1,000,000 lots compared to the long-term average of 700,000 lots.
Source: ASX data
Source: ASX data
Additionally, these improved market conditions have supported primary debt market issuance during the roll period. For evidence of this we have taken Treasury Bond tender data from the Australian Office of Financial Management (AOFM) for the period between September 2020 - the first roll period where reduced tick values (0.1bps for 10 Year Bond Futures and 0.2bps for 3 Year Bond Futures) and September 2025.
Between September 2020 and December 2024 (with reduced tick values but prior to de-linking), only 4 tenders were conducted during the 5-day quarterly roll period across 18 expiries.
In contrast, from March to September 2025 (post-de-linking), 4 tenders have already occurred within the roll period, across just 3 expiries.
Ultimately, the uptick in AOFM issuance over the roll period suggests that improved outright market liquidity has provided confidence among primary market participants (such as banks) to engage in tenders. This has resulted in the AOFM being more inclined to conduct tenders during the roll period, as reflected in the data.
Preserving roll market efficiency
ASX implemented the delinking initiative to strengthen outright market liquidity while preserving the efficient roll mechanics. This objective has been validated by the stability in the pace of quarterly roll dynamics and the continued consistency in Exchange for Physical (EFP) volumes, as observed in the charts below.
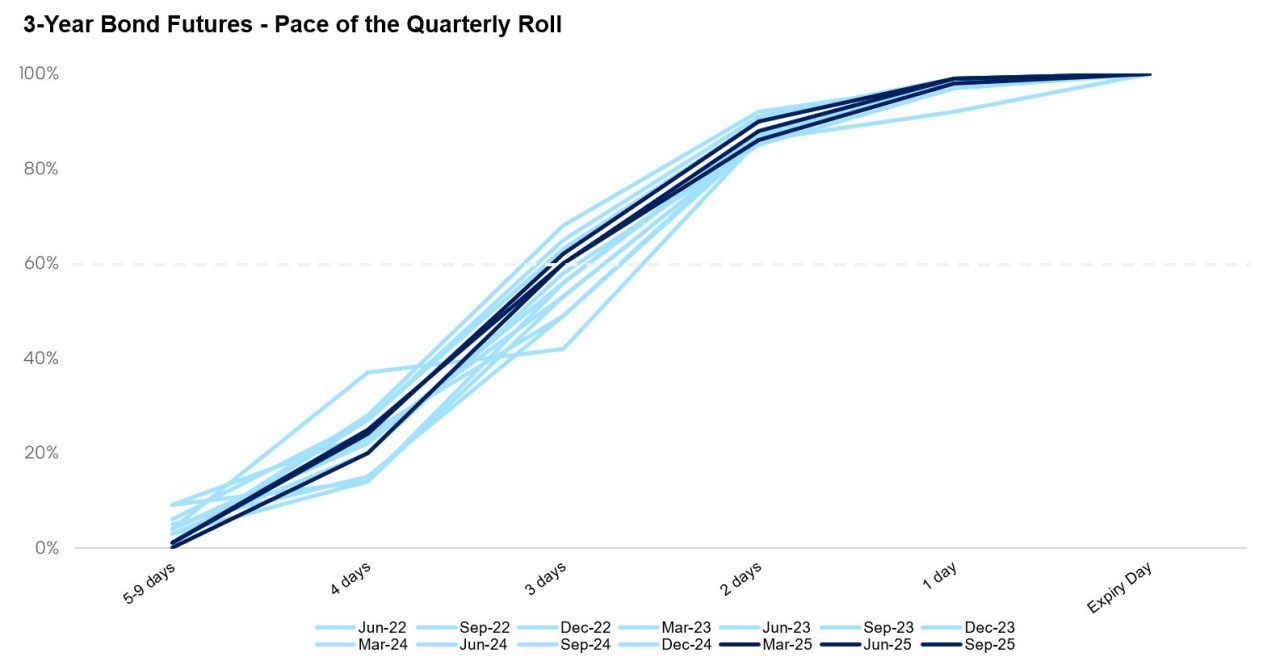
Source: ASX data
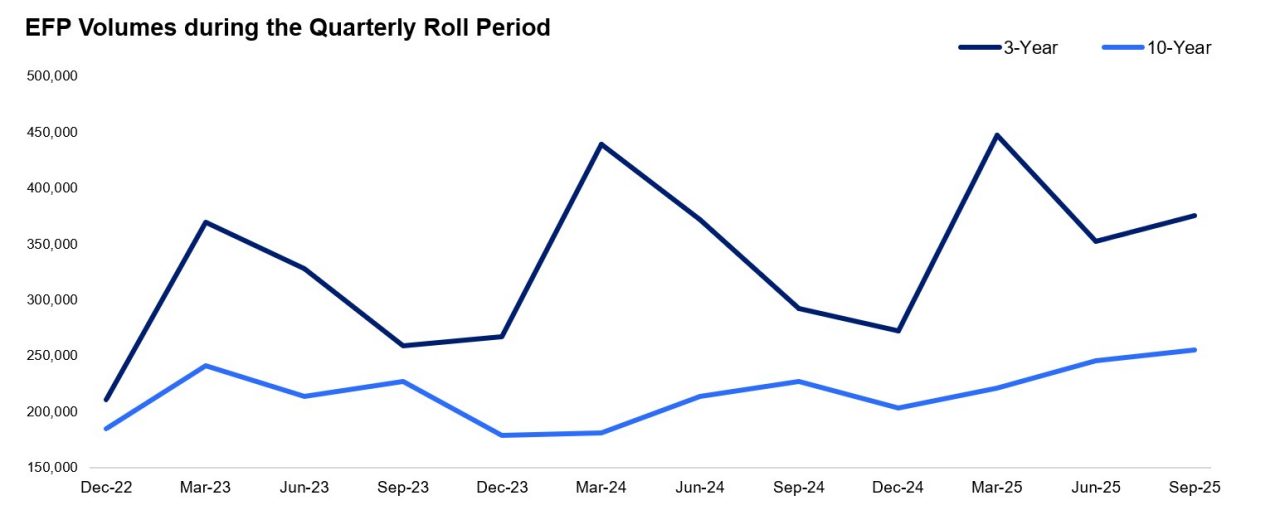
Source: ASX data
Roll activity is typically concentrated in the 5 business days leading up to the expiry of Bond Futures contracts, with volumes historically peaking on day 3. There has been an observed increase in total roll volume which primarily reflects higher open interest in ASX’s benchmark contracts, rather than any shift in trading behaviour. However, importantly, the pace of the roll remains steady and a majority of activity still occurring on day 3 based on a lookback period since June 2022. Furthermore, EFP volumes have remained broadly stable since 2023, showing no material change following the introduction of delinking. The only notable variation reflects the recurring seasonal uplift typically seen during March rolls in the 3-Year Bond Futures, consistent with historical patterns. Together, this reinforces that ASX has delivered market quality benefits without disrupting the mechanics or efficiency of the quarterly roll period.
International alignment
Exchange
| Product | Outright Tick Increment | Roll Tick Increment | Outright and spread market integration | Block Trades and Thresholds during Roll Period |
ASX | Australian Treasury Bond Futures | 3-Yr 0.5bps 10-Yr 0.5bps | 3-Yr 0.2bps 10-Yr 0.1bps | De linked calendar spread from outrights | No |
CME | US Treasury Futures | 2-Yr: 1/8 of 1/32 of one point 5-Yr: 1/4 of 1/32 of one point 10-Yr: 1/2 of 1/32 of one point | ¼ of 1/32nd of one futures price point | De linked calendar spread from outrights | No |
Eurex | German Bond Futures | Schatz 0.005% (EUR 5) Bobl/Bund 0.01% (EUR 10) | Same as outright | Integrated spread and outright market | Yes >2,000 lots 10 yr >3,000 lots 5 yr >4,000 lots 2yr |
ICE | UK Gilt Futures | Short/Med/Long: 0.01 (£10) | Same as outright | Integrated spread and outright market | Yes >3,000 lots <75, 000 lots |
TMX | Canadian Government Bond Futures | 2-Yr: 0.005 = C$5 5-Yr/10-Yr: 0.01 = C$1 | Same as outright | Integrated spread and outright market | No |
Major global interest rate futures markets differ in how they manage quarterly roll market microstructure. Some markets, such as the U.S. Treasury futures market, facilitate roll activity through Reduced Tick Spread (RTS) as a persistent functionality for calendar spread trading that allows finer price increments between contract months. In contrast, European and Canadian exchanges operate integrated markets, where calendar spread and outright trading share the same tick increment throughout the roll. However, these markets permit large-size block trade functionality during the roll period.
Through considering Australian market dynamics and engaging closely with industry participants, ASX has adopted a balanced and targeted approach under the Bond Futures Delink initiative by implementing the delink functionality only during the 5-days leading up to futures expiry. This approach recognises that while narrower tick sizes in calendar spreads enhance execution precision and flexibility during periods of heightened roll activity, it is equally important to support a robust and liquid trading environment for outright contracts.
Summary
To conclude, the implementation of the Bond Futures Delink initiative has garnered positive feedback from market participants, reflecting confidence in the new market structure. The initiative has delivered measurable improvements in outright market liquidity, depth and execution efficiency while preserving roll market efficiency. The alignment with global best practices reinforces ASX’s position as a competitive and resilient marketplace for interest rate risk management.
References
(1) Managing futures exposure - the quarterly futures roll explained - Jen Eason
(2) Back to the Futures: Liquidity in Australian Bond Futures amid Market-moving Events since COVID-19 - Richard Finlay, Ben Jackman and Dmitry Titkov
Other Insights
To receive regular insights via email, please subscribe to the ASX Rates Highlights quarterly newsletter.
Disclaimer
Information provided is for educational purposes and does not constitute financial product advice. You should obtain independent advice from an Australian financial services licensee before making any financial decisions. Although ASX Limited ABN 98 008 624 691 and its related bodies corporate (“ASX”) has made every effort to ensure the accuracy of the information as at the date of publication, ASX does not give any warranty or representation as to the accuracy, reliability or completeness of the information. To the extent permitted by law, ASX and its employees, officers and contractors shall not be liable for any loss or damage arising in any way (including by way of negligence) from or in connection with any information provided or omitted or from any one acting or refraining to act in reliance on this information.
© Copyright ASX Operations Pty Limited ABN 42 004 523 782. All rights reserved 2025.


