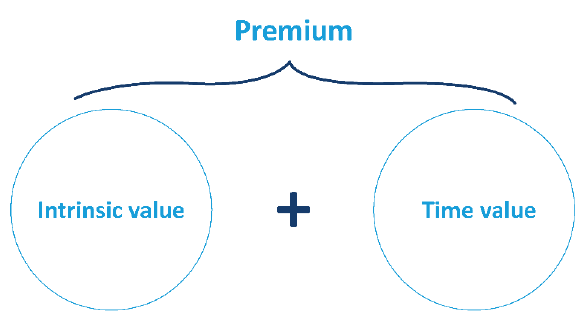
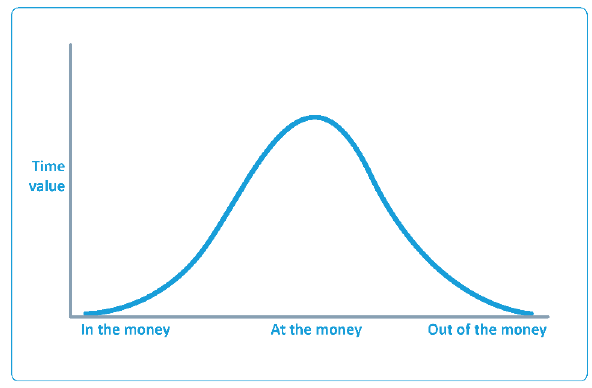
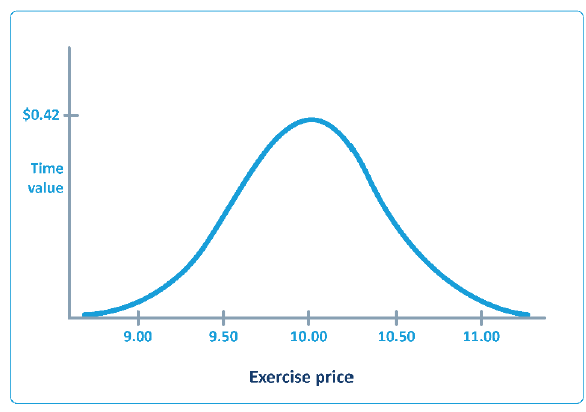
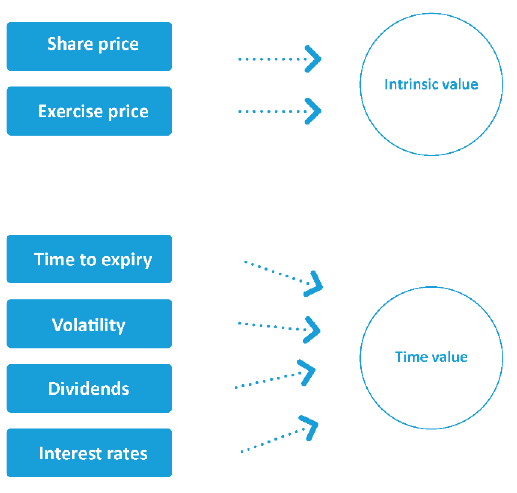
An option's premium comprises intrinsic value and time value.
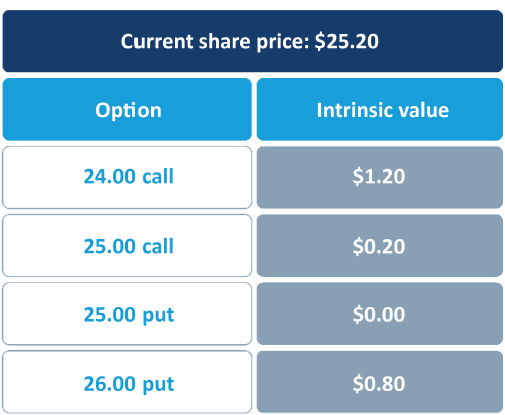
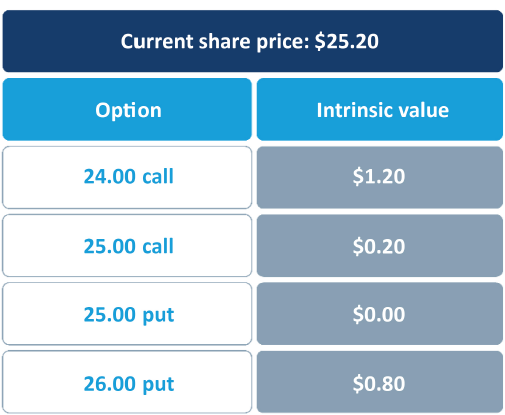
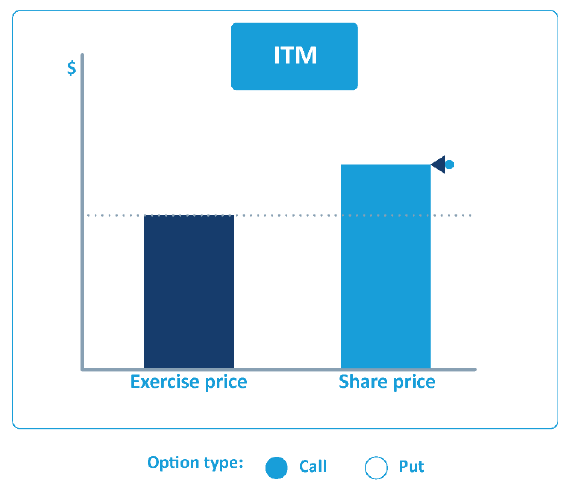
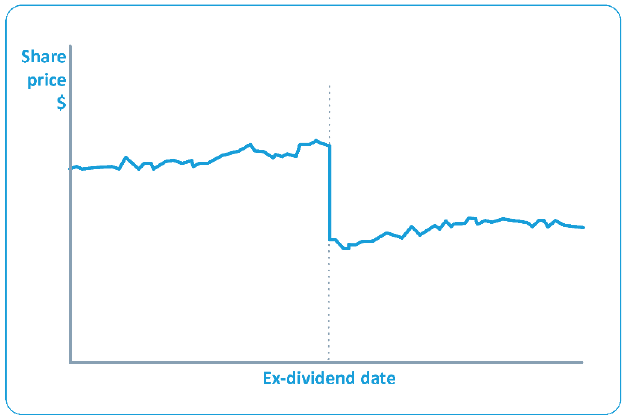
An option's intrinsic value is the difference between the exercise price and the current share price. A call has intrinsic value if the share price is above the strike price; a put has intrinsic value if the share price is below the strike price.
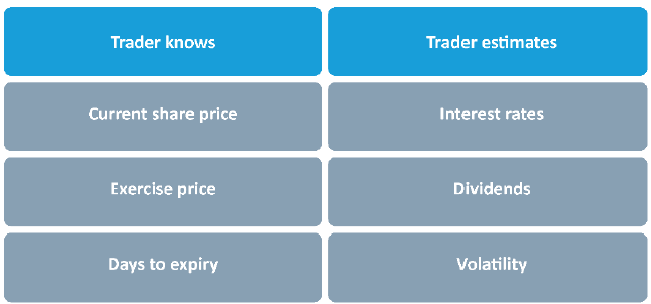
An option's time value is affected by:
- time to expiry
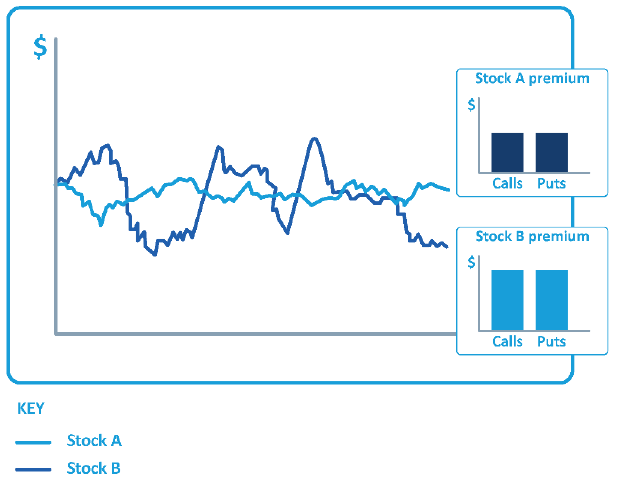
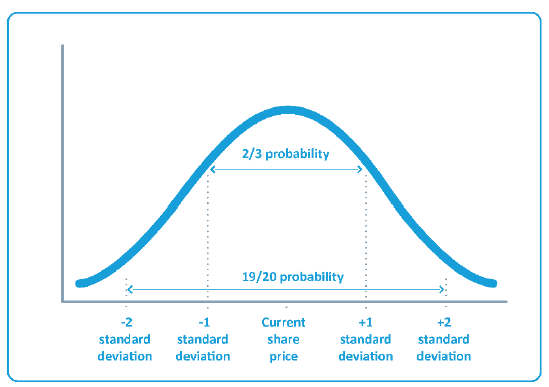
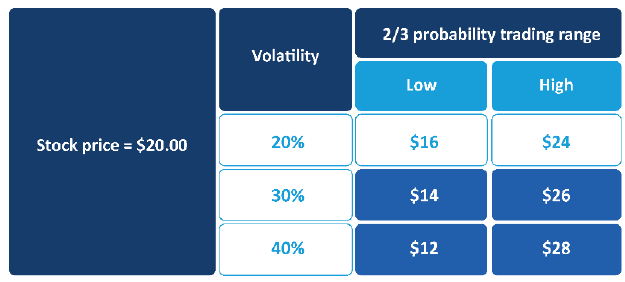
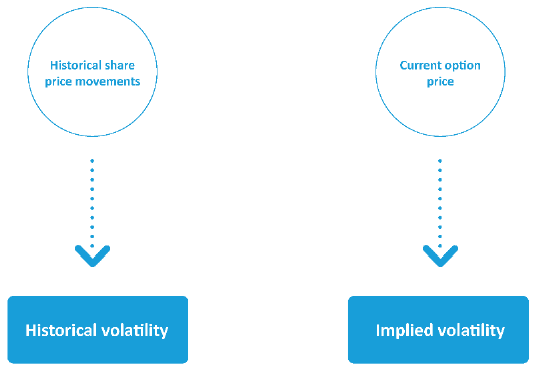
- volatility of the underlying shares
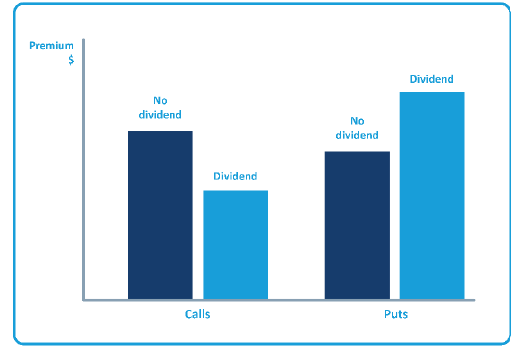
- dividends, and
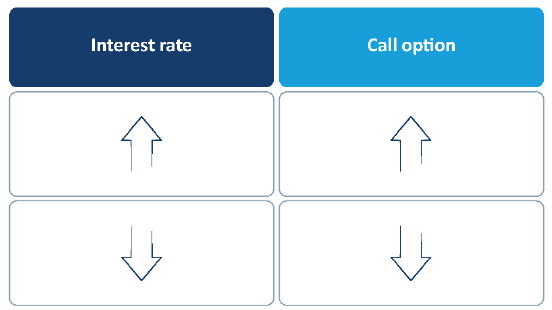
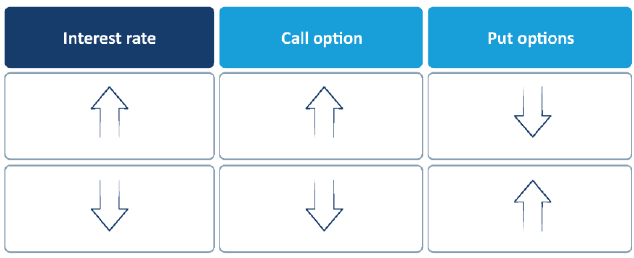
- interest rates.
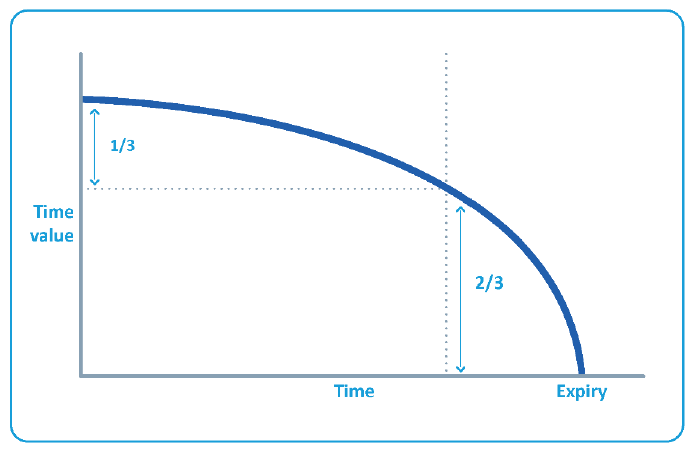
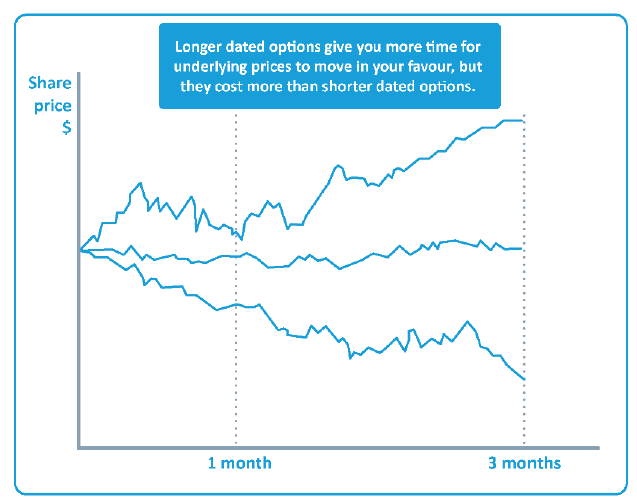
An option is a wasting asset. All other things being constant, as time passes, the time value of an option falls. At expiry, the option is worth intrinsic value only.
You can use an option pricing model to calculate an option's theoretical fair value. Pricing models produce values based on the variables that affect an option's premium.
The theoretical fair value is not necessarily the same as the option's market price.
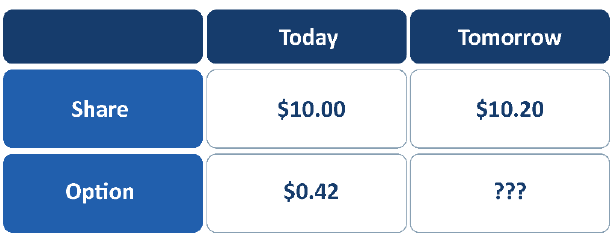
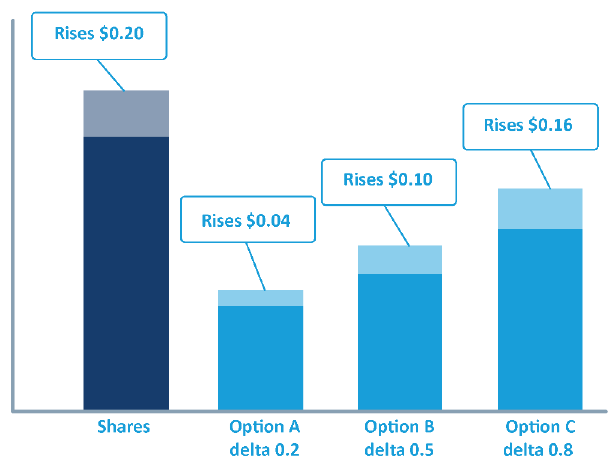
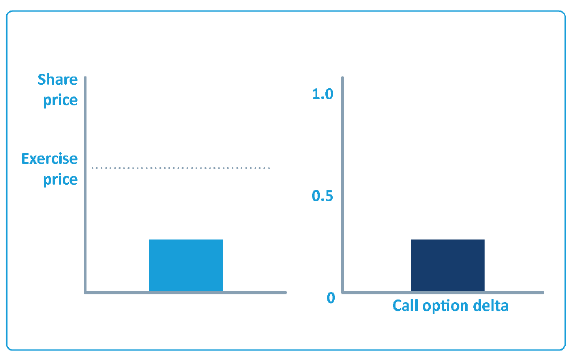
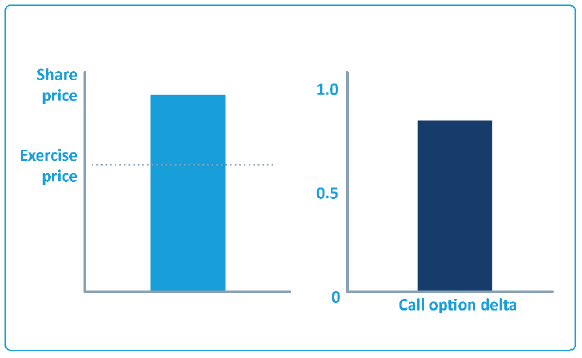
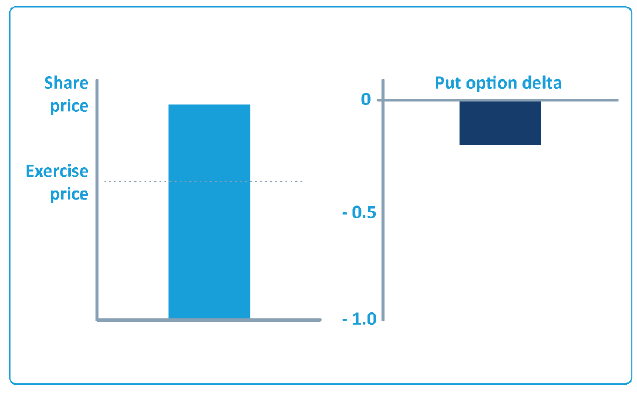
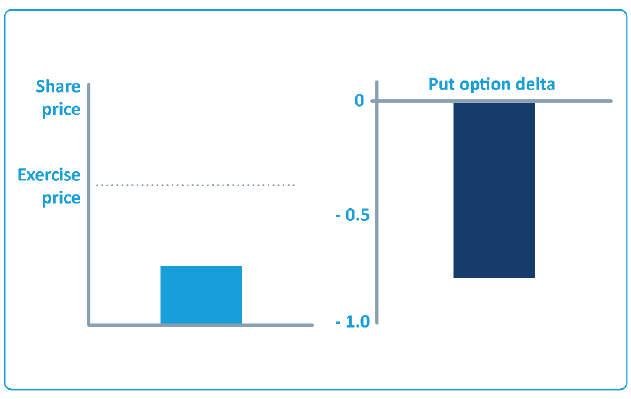
An option's delta indicates how the option will react to a change in the share price:
Change in option price = change in share price x delta
An option's delta is between 0 and 1. Call options have positive deltas, put options have negative deltas.